10 E-Commerce Customer Segmentation Strategies for 2025
In the crowded e-commerce landscape, treating all customers the same is a recipe for being ignored. The brands that thrive are those that understand their audience on a deeper level, delivering personalized experiences that resonate and build lasting loyalty. This is where customer segmentation strategies come in. By dividing your customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, behaviors, or needs, you can tailor your marketing, product recommendations, and loyalty programs with surgical precision. This approach not only boosts engagement and conversion rates but also significantly enhances customer lifetime value (CLV).
Forget generic, one-size-fits-all campaigns. Effective segmentation allows you to speak directly to specific customer motivations, whether you're welcoming a first-time buyer, re-engaging a lapsed VIP, or rewarding a brand advocate. The result is a more relevant and impactful customer journey that fosters genuine connection and drives repeat purchases.
This guide moves beyond the basics to provide a comprehensive roundup of 10 powerful segmentation models. We'll explore everything from foundational demographic and behavioral methods to advanced AI-driven predictive techniques, offering actionable insights and real-world examples for each. Whether you're launching your first loyalty program or refining a complex multi-channel strategy, these proven customer segmentation strategies will equip you to connect with your customers in more meaningful and profitable ways.
1. Demographic Segmentation: The Foundational Layer
Demographic segmentation is one of the most fundamental customer segmentation strategies, dividing your audience based on observable and quantifiable population characteristics. This approach organizes customers by data points like age, gender, income, education level, occupation, and family status. It serves as an essential starting point because this data is often readily available and directly correlates with customer needs and purchasing power.
This strategy provides a broad but crucial understanding of who your customers are. For an e-commerce brand, this knowledge informs a wide range of decisions, from the visual style of your marketing creative to the tone of your ad copy and the specific products you highlight.
How to Implement Demographic Segmentation
Implementing this strategy effectively goes beyond basic assumptions. Start by collecting data through your e-commerce platform, customer surveys, or analytics tools like Google Analytics.
- Actionable Example: A high-end skincare brand can use this strategy to great effect. They could segment their email list to target users aged 40-60 with higher reported incomes, promoting their premium anti-aging line. Simultaneously, they can market a more affordable, preventative skincare range to customers aged 20-30.
Pro Tip: Don't ask for all demographic information at once. Use progressive profiling in your loyalty program or email sign-up forms. Ask for a birthday one month to offer a discount, then later ask about family size to tailor product recommendations, making the data collection process feel less intrusive.
Layering demographic data with other segmentation types is where its true power emerges. Knowing a customer’s age is good, but knowing their age and their past purchase history is far more powerful for creating truly personalized and effective marketing campaigns.
2. Geographic Segmentation: Localizing Your Approach
Geographic segmentation involves dividing your audience based on their physical location. This can be as broad as a country or continent, or as granular as a city, zip code, or even climate zone. As one of the core customer segmentation strategies, it recognizes that customer needs, preferences, and purchasing habits are often heavily influenced by where they live.
This strategy is built on the principle that location dictates relevance. For an e-commerce store, knowing a customer’s location allows for tailored messaging, region-specific product offerings, and localized promotions that resonate more deeply than generic, one-size-fits-all campaigns.
How to Implement Geographic Segmentation
Start by leveraging location data from your e-commerce platform's shipping information, IP address tracking, or explicit data collection through sign-up forms. This data allows you to create targeted campaigns that reflect local culture, weather, or events.
- Actionable Example: An outdoor apparel retailer can use this strategy to promote different products based on real-time weather data. They could send an email blast advertising rain jackets to customers in Seattle while simultaneously marketing lightweight sun hoodies to shoppers in Phoenix. This ensures the marketing message is always timely and relevant.
Pro Tip: Don’t limit geographic segmentation to just marketing. Use it to optimize logistics. By analyzing customer density with GIS (Geographic Information System) tools, you can identify ideal locations for warehouses or fulfillment centers to reduce shipping times and costs, directly improving the customer experience.
Combining geographic data with other segmentation types creates a powerful, multi-layered view of your customer base. Understanding a customer’s location and their past browsing behavior is a winning formula for creating hyper-relevant and effective e-commerce experiences.
3. Psychographic Segmentation: Understanding the 'Why'
Psychographic segmentation moves beyond demographics to classify customers based on psychological traits like values, interests, lifestyles, and personality. This is one of the more nuanced customer segmentation strategies because it seeks to understand the motivations behind purchasing decisions. It answers the crucial question of why customers choose your products over others.

This strategy allows brands to create deeply resonant messaging that connects on an emotional level. For an e-commerce store, knowing a customer values sustainability is more powerful than just knowing their age, as it directly informs product recommendations, brand storytelling, and partnership choices. These psychographic segmentation examples showcase how brands can build a loyal community around shared values.
How to Implement Psychographic Segmentation
Implementing this requires qualitative data collection through surveys, customer interviews, and social media listening. Analyze reviews and feedback for recurring themes related to values or lifestyle.
- Actionable Example: An outdoor gear company can use this approach to connect with different types of adventurers. They could segment their audience into "Thrill-Seekers" who value performance and durability, and "Weekend Explorers" who prioritize comfort and convenience. The marketing for the first group would highlight ruggedness and extreme conditions, while the second group would see ads focused on family-friendly hikes and easy-to-use equipment.
Pro Tip: Use social media listening tools to monitor conversations and hashtags relevant to your industry. This can reveal emerging interests and values within your target audience, allowing you to adapt your segmentation and messaging in near real-time.
Combining psychographic insights with behavioral data creates a powerful, holistic view of the customer. Knowing someone is an eco-conscious consumer and that they consistently buy your recycled products allows for hyper-targeted loyalty rewards and content that reinforces their values and your brand's commitment.
4. Behavioral Segmentation: Understanding Customer Actions
Behavioral segmentation is one of the most powerful customer segmentation strategies because it groups customers based on their direct actions and interactions with your brand. This method moves beyond who customers are and focuses on what they do. It analyzes data points like purchase history, browsing patterns, product usage frequency, brand interactions, and loyalty status. This approach is highly actionable because it’s rooted in proven customer behavior, not assumptions.
This strategy provides a dynamic view of customer engagement and intent. For an e-commerce store, understanding these actions allows you to create timely, relevant, and automated marketing campaigns that respond directly to a customer's journey, from their first visit to their tenth purchase.
How to Implement Behavioral Segmentation
Effective implementation requires tracking user actions across all your digital touchpoints. Use your e-commerce platform's analytics, tools like Google Analytics, and your customer loyalty program to capture behavioral data.
- Actionable Example: Amazon excels at this. If a customer repeatedly views a specific product category but doesn't buy, Amazon sends automated browse abandonment emails featuring those exact items. Similarly, the Starbucks Rewards program segments users based on purchase frequency, offering personalized challenges and rewards to encourage more frequent visits and higher spending.
Pro Tip: Unify your data sources to get a complete picture. Integrate your online store, POS system, and loyalty app to track behavior across both online and offline channels. This allows you to reward a customer for an in-store purchase with a digital coupon, creating a seamless omnichannel experience.
Behavioral segmentation is the engine behind hyper-personalization. By understanding the actions that signal purchase intent, disengagement, or high loyalty, you can trigger the right message at the perfect moment to drive conversions and deepen customer relationships.
5. RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) Segmentation
RFM analysis is a powerful, data-driven model among customer segmentation strategies that evaluates and ranks customers based on their transaction history. This method assesses three key dimensions: Recency (how recently they purchased), Frequency (how often they purchase), and Monetary value (how much they spend). It's a proven model for predicting future engagement and identifying your most valuable customers.
This strategy helps you understand who your best customers are based purely on their buying behavior, allowing for highly targeted and cost-effective marketing. For an e-commerce store, this means you can focus your retention budget on customers most likely to deliver a high return.
How to Implement RFM Segmentation
Implementing RFM requires assigning a score (e.g., 1-5) to each customer for Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value. These scores are then combined to create distinct segments, like "champions" (high R, F, M) or "at-risk customers" (low R, high F/M).
- Actionable Example: An online pet supply store can use RFM to identify its "loyal customers" who purchase frequently but have a moderate monetary value (e.g., buying pet food monthly). They can send these customers automated reminders and exclusive access to new products. Conversely, they can target "hibernating" customers (low recency, high past value) with a compelling win-back offer to reactivate their spending.
Pro Tip: Define your RFM score thresholds based on your unique business cycle. For a mattress company, a purchase within the last year is recent, while for a coffee subscription, recency is measured in weeks. Update these scores at least monthly to ensure your segments reflect current customer behavior.
RFM provides a clear roadmap for prioritizing marketing efforts. By focusing on retaining your high-value segments and re-engaging those at risk, you can significantly boost customer lifetime value and create a more resilient business.
6. Needs-Based Segmentation: The "Why" Behind the Buy
Needs-based segmentation is a powerful approach among customer segmentation strategies, grouping customers according to the specific functional or emotional needs they are trying to fulfill. Instead of focusing on who the customer is (demographics) or what they did (behavioral), this strategy hones in on the core "why" driving their purchase decisions. It’s about understanding the fundamental problem a customer is trying to solve.
This method, heavily influenced by frameworks like Clayton Christensen’s "Jobs To Be Done," helps you align your product and messaging directly with customer motivations. For an e-commerce brand, this means you can speak to a customer's specific pain point, making your solution feel tailor-made for them.
How to Implement Needs-Based Segmentation
Implementation requires moving beyond quantitative data and into qualitative insights. Use customer interviews, focus groups, and surveys with open-ended questions to uncover the underlying reasons for their purchases.
- Actionable Example: An automotive parts retailer can use this to segment its audience. One group might be "Performance Enthusiasts" who need parts for speed and handling. Another could be "Safety-First Families" who need reliable brakes and tires. The marketing for each segment would be completely different, focusing on performance specs for the first group and durability and safety ratings for the second.
Pro Tip: Map your product features directly to the customer needs you've identified. Create a simple chart that lists each need (e.g., "reduce skin irritation") and then aligns the specific product features or ingredients that solve it (e.g., "oat extract, fragrance-free formula"). This makes creating targeted campaigns much easier.
By understanding customer needs, you can create more resonant messaging and innovate products that truly solve problems, fostering a deeper, more resilient form of customer loyalty.
7. Value-Based Segmentation (CLV): Focusing on Profitability
Value-based segmentation is a powerful approach that groups customers according to their economic value to your business, primarily using Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). This is one of the most strategic customer segmentation strategies because it helps you allocate resources where they will generate the highest return. Instead of treating all customers equally, you prioritize your most profitable ones.
This strategy answers the critical question of who your most valuable customers are, allowing you to invest in retaining them. For subscription services or retailers with frequent repeat purchases, this segmentation is essential for sustainable growth and maximizing profitability over time.
How to Implement Value-Based Segmentation
Begin by calculating CLV for your customer base, which typically involves historical purchase data and predictive analytics. Once calculated, group customers into tiers like high-value, mid-value, and low-value.
- Actionable Example: An airline can use CLV to identify its most profitable frequent flyers. This high-value segment receives exclusive perks like priority boarding, lounge access, and dedicated support lines. Meanwhile, lower-value, price-sensitive travelers might receive promotional emails about discounted fares, ensuring engagement across the entire spectrum.
Pro Tip: Align your loyalty program tiers directly with your CLV segments. Offer your most rewarding perks and exclusive experiences to the top-tier "VIP" customers to reinforce their value and encourage continued loyalty. This creates a clear path for mid-tier customers to increase their spending to unlock better rewards.
Value-based segmentation ensures your marketing budget and retention efforts are not just busy, but profitable. Focusing on your best customers is a direct path to boosting long-term revenue. To dive deeper into this metric, you can learn more about increasing customer lifetime value.
8. Technographic Segmentation: Adapting to Digital Habits
Technographic segmentation classifies customers based on the technology they use, such as their preferred devices, software, browsers, and digital platforms. This is one of the more modern customer segmentation strategies, essential for e-commerce brands operating in a multi-device world. It helps businesses understand their customers' technological preferences and digital fluency.
This strategy provides critical insight into how your customers interact with your brand online. For an e-commerce store, knowing if a customer primarily shops on an iPhone via Safari versus a Windows desktop using Chrome allows for tailored user experiences, optimized communications, and relevant technical support.
How to Implement Technographic Segmentation
Start by using analytics tools like Google Analytics or your e-commerce platform's built-in reporting to gather data on device usage, operating systems, and browser types. This data is often collected automatically and can be a goldmine for targeted marketing.
- Actionable Example: A SaaS company selling a design tool could segment its audience by operating system. It might promote its fully-featured desktop application to Windows and macOS users while directing its iOS and Android users to download its lighter, mobile-first companion app for on-the-go edits.
Pro Tip: Go beyond just the device. Segment users based on their engagement with specific tech-driven features. For instance, create a segment of customers who have used your AR "try-on" feature or those who consistently use a specific mobile payment option like Apple Pay, then tailor messaging to highlight related new technologies.
Technographic data is most powerful when combined with behavioral insights. Knowing a customer uses the latest iPhone is useful, but knowing they use it to browse your new arrivals within an hour of receiving a push notification is a highly actionable signal for a VIP segment.
9. Firmographic Segmentation: The B2B Blueprint
Firmographic segmentation is the essential B2B equivalent of demographic segmentation. This is one of the most critical customer segmentation strategies for businesses whose customers are other companies, dividing accounts based on firm characteristics. This approach organizes business customers by data points like industry, company size, annual revenue, geographic location, and ownership structure. It provides a foundational understanding of which companies are your best customers.
For a B2B e-commerce platform selling wholesale supplies or a SaaS company, this strategy is indispensable. It informs everything from your account-based marketing (ABM) efforts and sales outreach to the specific product bundles or service tiers you promote. Knowing a client is a small, high-growth tech startup versus a large, established manufacturing firm dictates a completely different approach.
How to Implement Firmographic Segmentation
Implementation starts with enriching your B2B customer data. You can gather this information from sign-up forms, sales team inputs, or by using third-party data enrichment tools that integrate with your CRM.
- Actionable Example: A software company like Salesforce uses firmographics to tailor its CRM offerings. It can target small businesses (10-50 employees) with a "Salesforce Essentials" bundle, while its enterprise sales team focuses on Fortune 500 companies with comprehensive, customized solutions. Similarly, LinkedIn Ads allows B2B marketers to precisely target professionals by industry, company size, and job function.
Pro Tip: Combine firmographic data with intent data for powerful account prioritization. Knowing a company fits your ideal size and industry profile is good, but knowing that same company is actively researching solutions like yours (intent data) signals they are a high-priority, sales-ready lead.
Firmographic segmentation provides the "who" and "where" of your B2B audience. Layering it with behavioral or technographic data creates a highly-focused and effective strategy for acquiring and retaining high-value business accounts.
10. Predictive (AI-Driven) Segmentation
Predictive segmentation represents the frontier of customer segmentation strategies, using machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to forecast future customer behavior. Instead of grouping customers based only on past actions, this approach analyzes vast datasets to identify patterns and predict outcomes like churn risk, lifetime value, and the likelihood to purchase specific products. This method creates dynamic, self-optimizing segments that evolve with customer behavior.
This strategy answers the crucial question of what your customers will do next. For an e-commerce store, this forward-looking insight allows for proactive, highly personalized marketing. You can identify at-risk customers before they leave and target high-potential customers with upsell opportunities before they even search for a product. To further explore the practical applications of AI in customer engagement, consider resources focused on AI marketing strategies.
How to Implement Predictive Segmentation
Implementing this strategy involves leveraging AI tools to analyze your customer data for hidden correlations. The goal is to build models that score customers on various potential actions, enabling you to segment them based on future probabilities rather than just historical data.
- Actionable Example: An online fashion retailer like Stitch Fix uses predictive models to analyze customer style quizzes, purchase history, and feedback. The AI predicts which new clothing items a customer is most likely to love and keep, allowing the company to curate highly personalized subscription boxes that drive satisfaction and reduce returns.
The following concept map visualizes how AI algorithms process data to create and update these dynamic segments in real time.
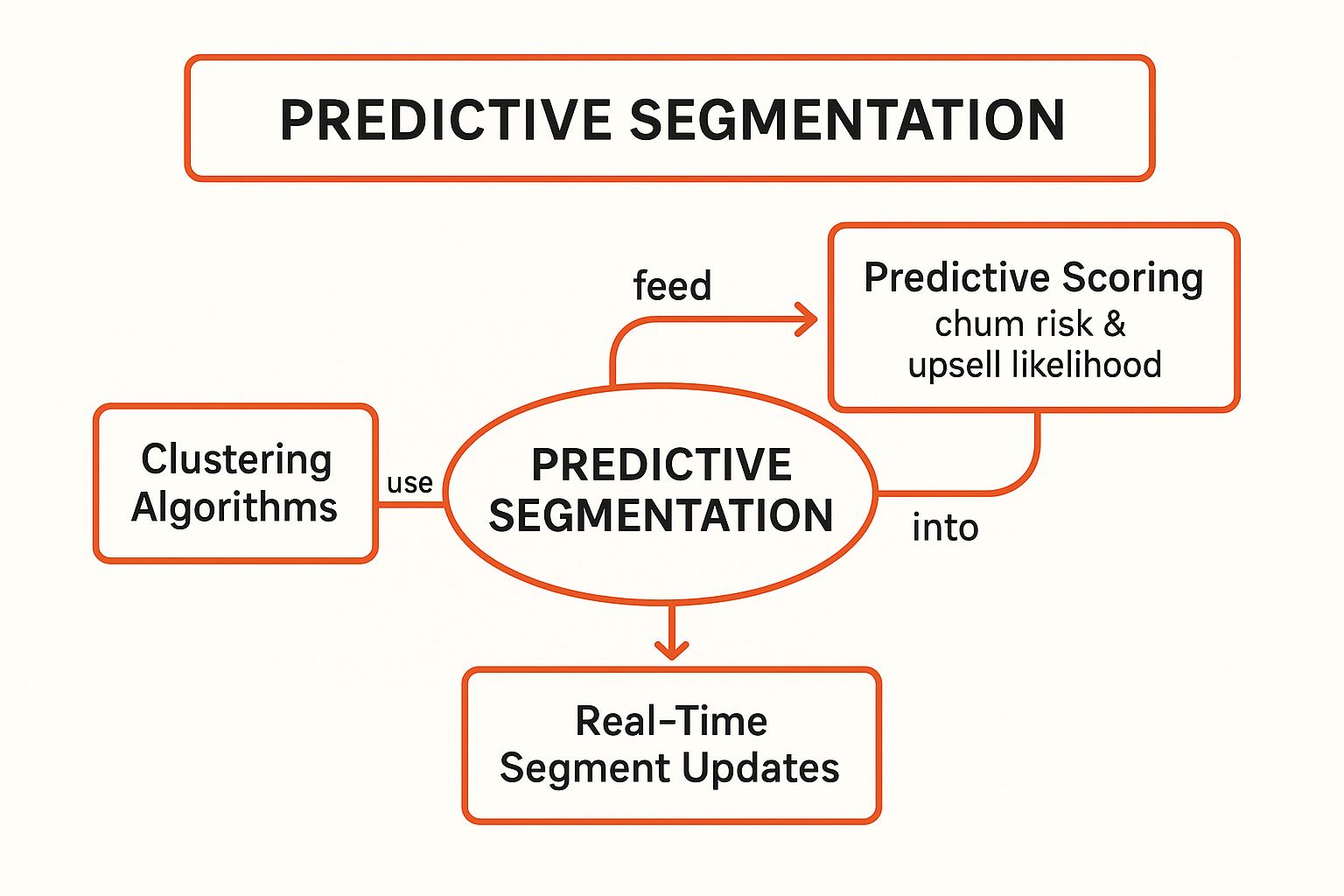
This process shows a continuous loop where clustering algorithms identify patterns, which then inform predictive scores for churn and upsells, leading to real-time adjustments of customer segments.
Pro Tip: Start small with predictive modeling. Begin with a pilot project focused on a single, high-impact outcome, such as identifying customers likely to churn in the next 30 days. Validate your model’s predictions against actual results before scaling the strategy across your entire customer base.
By forecasting behavior, predictive segmentation empowers brands to move from reactive to proactive marketing, significantly enhancing customer retention and lifetime value. Learn more about using machine learning to boost customer loyalty.
Customer Segmentation Strategies Comparison
| Segmentation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Segmentation | Low - straightforward, widely available | Low - easy data collection | Basic customer grouping; broad targeting | Initial segmentation, mass market strategies | Simple, affordable, easy to analyze |
| Geographic Segmentation | Low to Medium - depends on granularity | Medium - GIS tools and location data | Localized marketing and inventory planning | Regional promotions, location-based offers | Enables geo-targeted campaigns |
| Psychographic Segmentation | High - requires qualitative research | High - surveys, focus groups, social listening | Deep customer insights; value-based targeting | Brand positioning, loyalty programs | Highly tailored messaging and long-term loyalty |
| Behavioral Segmentation | Medium to High - needs tracking systems | Medium to High - data capture across channels | Personalized offers; predicts short-term sales | E-commerce promotions, loyalty programs | Actionable and dynamic based on real behavior |
| RFM Segmentation | Medium - relies on clean transactional data | Medium - requires transaction databases | Quantitative ranking for engagement and profitability | Targeted re-engagement campaigns | Data-driven, effective for retention efforts |
| Needs-Based Segmentation | High - deep qualitative research | High - ethnographic studies, interviews | Aligns messaging with customer motivations | Product development, value proposition design | Focused on core customer needs |
| Value-Based Segmentation | High - complex data integration | High - finance and marketing data combined | Optimizes ROI by prioritizing valuable customers | Retention vs. acquisition resource allocation | Maximizes marketing efficiency |
| Technographic Segmentation | Medium to High - tech data and privacy issues | Medium to High - device/software usage data | Technology-driven offers; IT decision-maker targeting | B2B tech vendors, app usage segmentation | Targets customers by tech usage |
| Firmographic Segmentation | Medium - B2B focused with vendor data | Medium - industry and company databases | Improves lead scoring and account targeting | B2B sales and marketing | Focuses on company attributes for ABM |
| Predictive Segmentation | Very High - requires data science expertise | Very High - ML infrastructure and monitoring | Dynamic, adaptive segments; uncovers hidden patterns | AI-driven personalization, churn prediction | Highly personalized and self-optimizing |
From Strategy to Action: Building a Unified Customer View
We've explored a comprehensive toolkit of ten distinct customer segmentation strategies, moving from foundational models like demographic and geographic to more sophisticated approaches such as predictive AI and value-based segmentation. Each strategy offers a unique lens through which to view your audience, but the true power lies not in isolation, but in integration. The most successful e-commerce brands don't just pick one method; they skillfully weave them together to create a rich, multi-dimensional, and actionable understanding of their customer base.
This journey from raw data to deep insight is a progressive one. You might begin with the broad strokes of demographic and firmographic data to understand who your customers are and where they come from. From there, you can layer on behavioral and RFM analysis to illuminate what they do, how often they engage, and how much they spend. The final, most impactful layers often come from psychographic and needs-based segmentation, which help you connect with the crucial why behind their actions.
Key Takeaways for E-commerce Growth
The ultimate goal is to evolve beyond static, one-dimensional lists. A dynamic, unified customer view allows you to anticipate needs, personalize interactions, and build genuine, lasting loyalty. Consider these core principles as you move forward:
- Start Small, Scale Smart: You don't need to implement all ten strategies at once. Begin with a foundational model like behavioral or RFM segmentation. Measure the impact on engagement and sales, then progressively add new layers of data to refine your approach.
- Data is Your Foundation: The quality of your segmentation is directly tied to the quality of your data. Ensure you have systems in place to collect clean, accurate, and relevant information across all customer touchpoints, from website activity to loyalty program engagement.
- Action is the Goal: Segmentation without action is just an academic exercise. Once robust segmentation strategies are in place, the next crucial step is leveraging these insights for practical applications, such as developing effective customer personalization strategies that make each customer feel seen and valued.
- Embrace Dynamic Segmentation: Customers are not static. Their needs, behaviors, and value to your business will change over time. Your segmentation model should be fluid, allowing customers to move between segments as their relationship with your brand evolves.
Mastering these powerful customer segmentation strategies is the key to unlocking sustainable growth. It's the difference between shouting into the void and having a meaningful conversation with the people who matter most to your business. By committing to truly knowing your customers, you lay the groundwork for exceptional personalization, increased customer lifetime value, and a brand that inspires genuine loyalty.
Ready to turn segmentation theory into profitable action? Toki provides the all-in-one platform to build, manage, and scale your loyalty and engagement programs. Use our powerful tools to implement behavioral, value-based, and tiered segmentation that drives repeat purchases and builds a thriving community around your brand. Explore Toki today and start building deeper customer relationships.